Resistant Depression: What It Is, Symptoms, and Treatment
Sometimes, treatment for depression doesn't work, and it's time to consider other options. Discover what resistant depression is and how to treat it.
Resistant depression is more common than you might think. Data indicates that around 15% of people experience depression at some point in their lives. Of these individuals, 20% do not respond well to treatment, but that doesn't mean there's nothing that can be done. Explore what resistant depression is and what innovative treatments are already available.
What Is Resistant Depression?
Resistant depression refers to a type of depression that does not adequately respond to conventional treatments. It involves symptoms typically associated with depressive disorders, such as persistent feelings of sadness, lack of interest in previously enjoyable activities, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, changes in sleep and appetite, among others.
Usually, depression is successfully treated through a combination of psychotherapy, antidepressant medications, and lifestyle changes. However, when a patient does not improve even after trying at least two different treatments for an appropriate period with adherence to the treatment plan, they are considered to have resistant depression.
In some cases, resistant depression can be life-threatening. A person who is deeply depressed may feel so desperate that they contemplate or even attempt suicide as a way to alleviate emotional pain. Therefore, depression should not be underestimated, and it is essential to seek medical and psychological help as soon as depressive symptoms are identified.
What Are the Main Causes of Resistant Depression?
These are some of the primary reasons why depression becomes resistant to treatment.
- Biological Factors
Some patients may have a genetic predisposition to depression, making treatment more challenging.
- Brain Changes
Depression is often associated with imbalances in brain chemicals, such as low levels of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. In cases of resistant depression, these changes may be more pronounced or less responsive to medications. - Comorbidities
The presence of other physical or mental illnesses, such as bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, substance abuse, or chronic diseases, can complicate the treatment of depression.
- Inadequate Treatment History
Initial inadequate treatment of depression, including the improper use of medications or a lack of therapeutic follow-up, can lead to an inadequate response to treatment and, consequently, the development of resistant depression. - Chronic Stress
People exposed to high levels of chronic stress, such as financial problems, family conflicts, or trauma, may have a higher likelihood of developing resistant depression.
- Non-Adherence to Treatment
Not following medical advice or prematurely discontinuing the use of antidepressant medications or therapy can contribute to treatment resistance.
- Psychosocial Factors
Social issues, such as isolation, lack of support, or difficulties in work and relationships, can also compromise treatment response.
What Are the Symptoms of Resistant Depression?
The symptoms of resistant depression are similar to those of common depression, differing only in their persistence or inadequate response to conventional treatments. Typical symptoms of resistant depression may include:
- Constant feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or emptiness.
- Perpetual extreme fatigue and lack of energy.
- Excessive self-criticism and feelings of worthlessness.
- Difficulty concentrating and making decisions.
- Inability to experience interest or pleasure in once-enjoyable activities.
- Trouble sleeping or excessive sleepiness.
- Significant weight loss or gain unrelated to diet or exercise.
- Recurrent thoughts of death, suicide, or a desire to cease existing.
- Physical symptoms without a clear medical origin, such as chronic pain, gastrointestinal problems, among others.
How Is Resistant Depression Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of resistant depression should be made by a psychiatrist and begins with a comprehensive and detailed interview to understand the symptoms, medical history, and potential risk factors or comorbidities.
The healthcare professional may conduct some tests to rule out other conditions that may be causing the symptoms, such as thyroid disorders or bipolar disorder. It is also necessary to evaluate the patient's treatment history, including the types of antidepressant medications and therapies previously attempted, as well as the duration and adherence to treatments.
Next, the psychiatrist may arrive at the final diagnosis of resistant depression when the patient does not respond adequately to at least two different treatments administered at appropriate doses and for a sufficient duration.
What Does Resistant Depression Treatment Involve?
Treating resistant depression is especially challenging, considering that previous therapies have not been effective. However, it does not mean that treatment is impossible.
Currently, there are additional and innovative therapeutic approaches that can be considered when depression resists treatment. The psychiatrist may prescribe one or more of the following options:
- New Medications
In some cases, the psychiatrist may prescribe different medications than those previously attempted to treat depression, or less common ones compared to traditional antidepressants. For example, it may be helpful to use cutting-edge medications such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors or atypical antidepressants.
Additionally, combining atypical antipsychotics with certain antidepressants may help improve depressive symptoms, especially in severe cases. It is up to the doctor to assess the risks, benefits, drug interactions, and the specific needs of each patient.
- More Intensive or Different Oriented Psychotherapy
Resistant depression is profoundly debilitating, so it may be essential to increase the frequency of psychotherapy sessions to allow for deeper work and provide more support during crisis periods.
Moreover, there are several psychotherapeutic approaches, each with specific principles and techniques, and the patient may need an approach that is more compatible with their needs. For example, cognitive-behavioral therapy focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought and behavior patterns, while psychodynamic therapy explores unconscious dynamics and interpersonal relationships in depth. Exploring a different therapeutic orientation can be crucial in finding the most effective approach to treating resistant depression. In any case, the quality of the patient-therapist relationship is always the primary factor in the success of treatment.
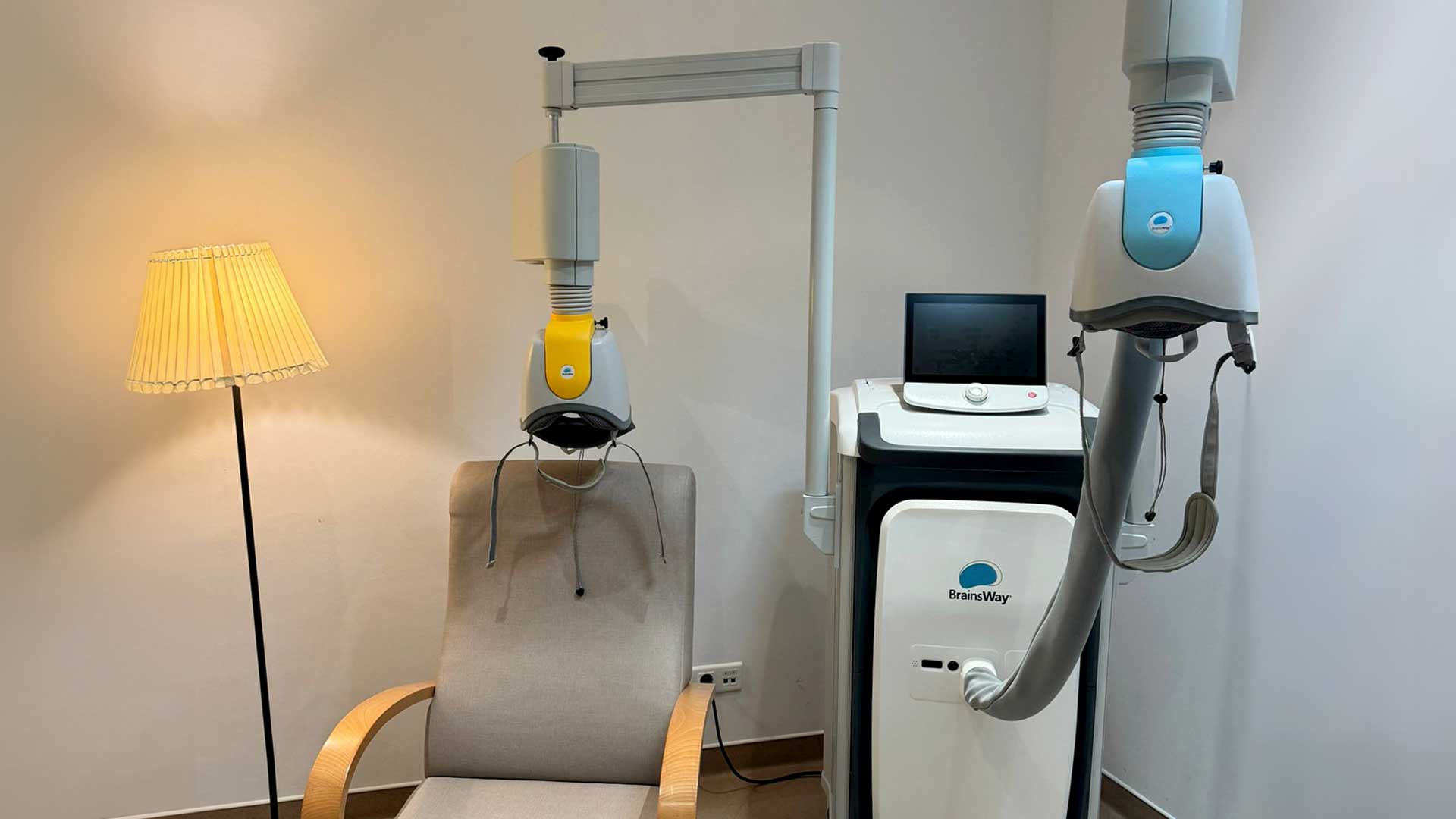
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation is an innovative, painless, and effective treatment for resistant depression. It is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique in which the patient places their head against a device that stimulates specific brain areas.
Anesthesia is not required, and no significant side effects have been reported. Occasionally, mild and temporary symptoms may occur, such as headaches or dizziness, which resolve within minutes. This procedure is performed in a clinical setting and does not require hospitalization.
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
This medical intervention involves the controlled application of an electric current to the brain under general anesthesia in multiple sessions. The goal is to stimulate the action of certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, involved in resistant depression.
Electroconvulsive therapy has been the subject of controversy, especially due to historical concerns about safety and misuse. However, over the years, the scientific understanding of this treatment has significantly evolved, making it safer, more effective, and less traumatic for patients. It may even be especially important in situations with a risk of suicide.
- Esketamine
Esketamine is a new medication that has been widely investigated and used as an innovative treatment option for resistant depression. It is administered exclusively in a hospital setting, under medical supervision, through nasal spray, with a fast onset of action and tolerable side effects.
- Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in the treatment and management of resistant depression. Establishing and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits can complement psychotherapeutic and pharmacological interventions, providing a solid foundation for emotional well-being. Often overlooked habits, such as nutrition guided by a Nutrition professional, personalized regular physical exercise, and good sleep hygiene, can have a significant impact on reducing depressive symptoms.
Joaquim Chaves Saúde: Your Partner in Resistant Depression Treatment
It is essential to seek professional help as early as possible to prevent the worsening of symptoms. With the right treatment and multidisciplinary support, it is possible to achieve better symptom management and regain a higher quality of life. At Joaquim Chaves Saúde, you will benefit from the most advanced therapeutic protocols to successfully address the challenges of resistant depression. Schedule your consultation now through the personal area of the website or our app.