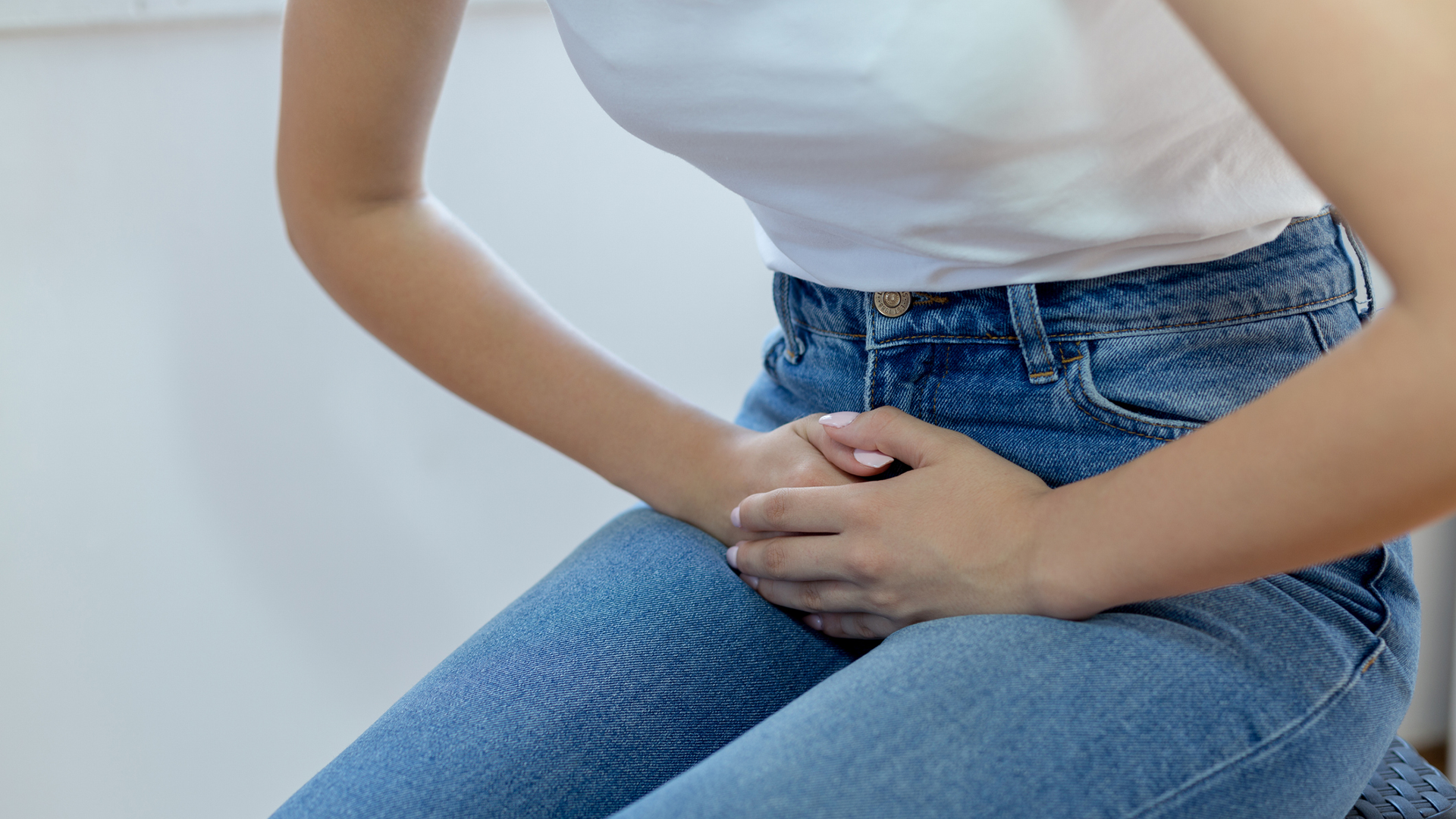
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) can cause great discomfort, but the treatment is simple and fast. Find out what this condition is, causes and symptoms, treatment and prevention.
What is a urinary tract infection?
The term urinary tract infection (UTI) refers to the presence of bacteria in any part of the urinary system, whether kidneys, urethra and bladder. Microorganisms enter from outside the body, via the urethra or, more rarely, through the blood. These bacteria are usually eliminated by the body’s defences or urine, but when this does not happen, it causes a urinary tract infection.
What are the types of urinary tract infection?
Urinary tract infections are classified according to the area affected.
Cystitis
This infection occurs in the bladder and is the most common type of UTI. Cystitis usually causes symptoms like pain while urinating, an urgent and frequent need to urinate, as well as a feeling of full bladder even after urinating.
Urethritis
Urethritis occurs in the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. This infection can cause pain or a burning sensation while urinating.
Pyelonephritis
This is the most serious type of urinary tract infection. It occurs in the kidneys and causes back pain, fever and intense general discomfort.